IN THIS ARTICLE
When concrete slabs settle or become sunken or uneven in the Philadelphia area, it can create various safety hazards, dangers, and structural issues. Here are some potential hazards that can arise from the concrete settlement:
- Tripping and Falling: Uneven concrete surfaces, such as sidewalks, driveways, and patios, can create tripping hazards for pedestrians. Uneven concrete can cause falls, especially for older people, children, or those with mobility issues, due to sudden changes in height.
- Sunken driveways and parking areas can damage vehicles by scraping against the ground or causing jolts on uneven surfaces. This can result in damage to the vehicles’ undercarriage, tires, and suspension systems.
- Water Drainage Issues: Settlement in concrete surfaces can disrupt the natural flow of water, causing puddles, ponding, and poor drainage. Accumulating water can lead to erosion, soil erosion, and potential foundation problems if water infiltrates the underlying soil.
- Sunken concrete can weaken buildings and structures if it affects the foundation or load-bearing parts, causing structural instability. This could lead to cracks in walls, floors, and ceilings, as well as compromised stability over time.
- Aesthetic and Property Value Concerns: Uneven or sunken concrete can detract from the visual appeal of a property. This could potentially reduce its curb appeal and property value, making it less attractive to potential buyers or tenants.
- Accessibility Issues: Sunken concrete can create accessibility challenges for individuals with disabilities. Wheelchair users, for example, may find it difficult or impossible to navigate areas with uneven surfaces.
- Damage to Infrastructure: Sunken or uneven concrete can impact adjacent infrastructure such as utility lines, drainage systems, and landscaping. It might also affect the stability of nearby structures.
- Property owners must be responsible for injuries caused by hazards on their property, like tripping on uneven concrete. Legal actions resulting from injuries can lead to financial burdens and reputational damage.
To mitigate these hazards, it’s important to address concrete settlement issues promptly. You can fix the settlement by mud jacking, replacing the concrete, or using other repair methods. The severity of the settlement and its cause will determine the best approach.
Regular inspections and maintenance of concrete surfaces can help prevent hazards from arising in the first place. If you notice signs of concrete settlement or hazards on your property, it’s advisable to consult with a professional concrete repair contractor to assess the situation and recommend appropriate solutions.
What is Mud Jacking-
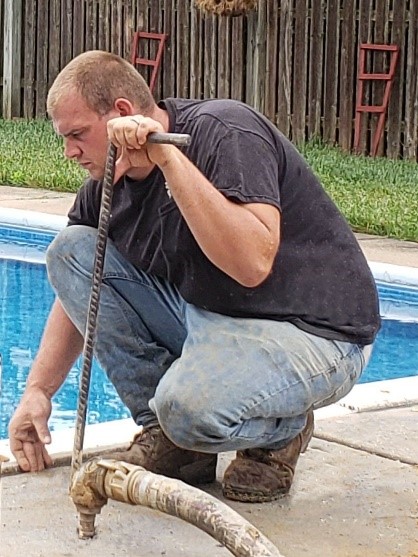

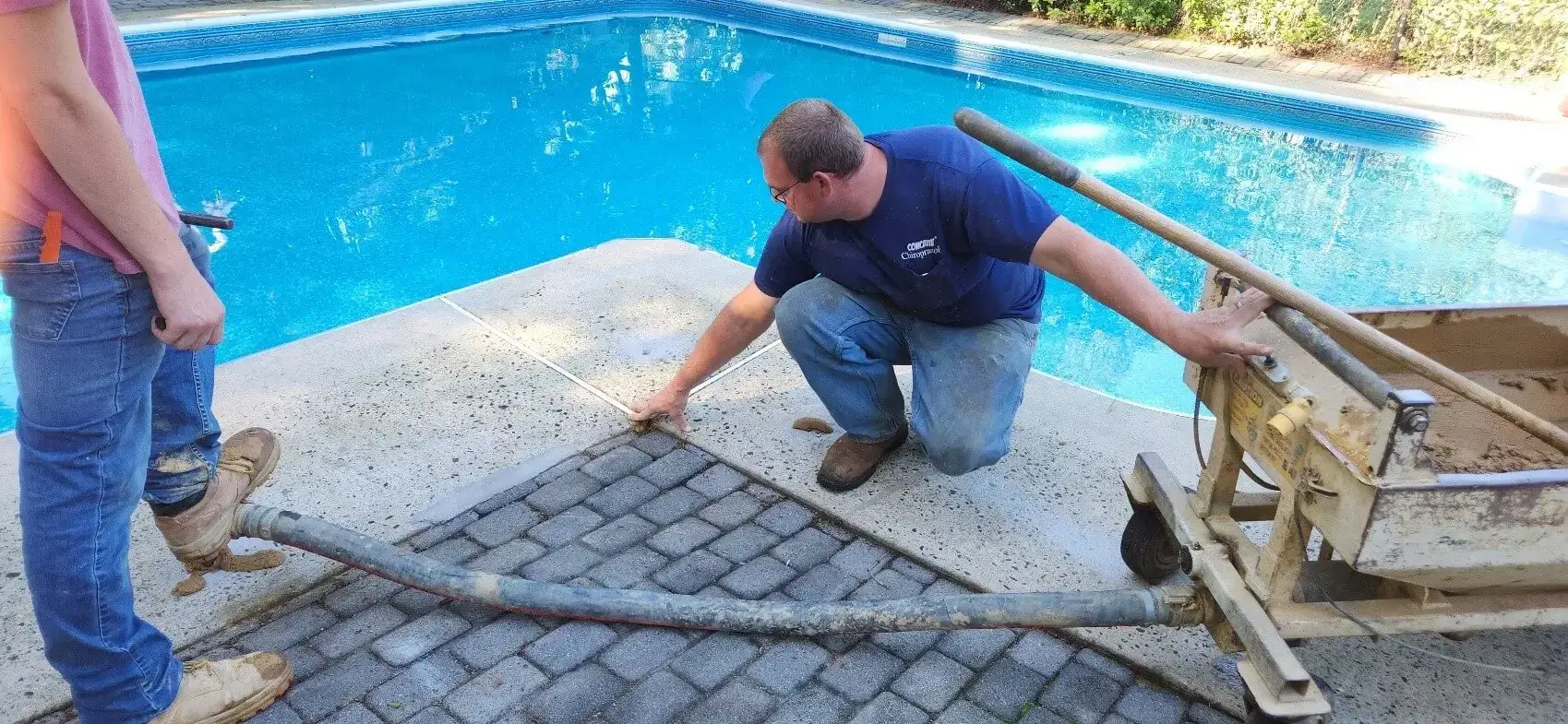
Mud jacking is a technique used to elevate and stabilize uneven or sunken concrete slabs in construction and foundation repair, also known as slab jacking or concrete lifting.
This procedure is commonly employed to rectify concrete surfaces that have descended or settled, such as sidewalks, driveways, patios, and foundations. The descent or settling is typically due to soil erosion, inadequate compaction, or other contributing factors.
The technique involves the injection of a grout mixture (a slurry of water, soil, cement, and other additives) beneath the sunken concrete slab. This injected grout fills the gaps in the soil underneath the slab, offering support and raising the slab back to its initial level. Over time, the grout solidifies, providing a firm base for the concrete surface.
A newer method that entails the blending and infusion of a dual-component chemical substance is referred to as polyurethane foam concrete lifting or poly foam. Nonetheless, these oil-derived products carry inherent dangers and expenses due to their combustibility, harmfulness, and problems related to recycling.
The History of Mud Jacking-
Mudjacking, also known as slab jacking, concrete lifting, or concrete leveling, is a technique used to raise and align sunken or uneven concrete surfaces by injecting a mixture of materials beneath the slab. This approach has been employed for numerous years to fix and revive various kinds of concrete constructions. These constructions encompass walkways, driveways, outdoor living spaces, and even certain minor foundation repairs.
Now, let’s take a look at the history of mud jacking. Here’s a summary of the mud jacking history.
Initial Stages: The idea of mud jacking has its roots in the early 1900s. During the 1920s and 1930s, engineers and construction experts started exploring various techniques to tackle the problem of sinking or settled concrete slabs. The main driving force was to discover an economical way to fix and level these surfaces without resorting to significant demolition and replacement.
Origination and Initial Application: The creation of mud jacking cannot be attributed to a single person. Instead, it’s thought to have been developed as a practical answer to a problem through the combined efforts of engineers, contractors, and construction workers. The procedure involves drilling holes into the depressed concrete and then pumping a slurry mixture—usually a blend of water, soil, and cement—into these holes. The slurry fills the gaps under the slab, lifting the concrete to the required height.
Evolution and Broad Acceptance: The effectiveness and efficiency of mud jacking have improved over time due to advancements in materials and techniques. The mid-20th century saw a surge in the use of mud jacking as a repair method, coinciding with the rise of concrete construction. The process was fine-tuned by contractors and specialists, incorporating better equipment, more precise injection methods, and improved slurry mixtures.
Modern Applications: In recent years, there have been some new developments in the field of mud jacking, with the incorporation of new technologies and materials.
Limitations and Alternatives: Mud jacking, while a feasible option for certain concrete repair situations, is not suitable for all. For instance, severely damaged or deteriorated concrete may require complete replacement. Moreover, mud jacking might not be the best solution for more serious foundation issues.
In Conclusion: Mudjacking, an economical method for lifting and stabilizing sinking concrete surfaces, has been utilized for numerous years. While the basic principles of the technique remain unchanged, advancements in materials and equipment have boosted its efficiency and effectiveness. As the realm of construction and repair technology advances, it’s probable that mudjacking will continue to evolve and retain its place among the various choices for concrete repair and renovation.
The Mud Jacking Process-
- Assessment and Preparation:
-
- A professional mudjacking contractor assesses the sunken or uneven concrete surface to determine the extent of the problem and whether mudjacking is a suitable solution.
- The contractor identifies the areas that need to be lifted and levels of settlement.
- Drilling Holes:
-
- Once the assessment is complete, the contractor marks the areas where holes need to be drilled.
- Small holes (usually around 1 inch in diameter, or the size of a quarter) are drilled into the sunken concrete slab. These holes are strategically placed to access the voids or spaces beneath the slab.
- Injection of Slurry:
-
- A slurry mixture is prepared. Traditionally, this slurry consists of a mix of water, sand or limestone, and cement. In modern applications, polymer-based materials might also be used for their lightweight and high-strength properties.
- The slurry is pumped under pressure through the drilled holes into the voids beneath the sunken concrete.
- Lifting and Leveling:
-
- As the slurry is injected, it fills the voids and exerts pressure against the underside of the slab.
- The pressure from the injected slurry gradually lifts the sunken concrete slab to its desired level. Contractors monitor this process carefully to ensure that the slab is lifted uniformly and to the correct elevation.
- Hole Sealing and Cleanup:
-
- After the concrete slab has been lifted and leveled, the drilled holes are sealed using cement materials.
- Any excess slurry that might have oozed out during the injection process is cleaned up.
- Curing and Use:
-
- The repaired concrete surface is typically usable shortly after the mudjacking process is completed. However, slabs subject to vehicle traffic may take a couple of days.
- Allow the repaired area to cure properly before subjecting it to heavy loads or traffic.
- Constraints and Factors to Consider:
- Not suitable for severely damaged concrete: Mudjacking might not be effective if the concrete is heavily cracked, deteriorated, or structurally compromised. The concrete may re-settle due to the same issues, potentially leading to future settling.
- Aged concrete can be as durable as new replacements. The underlying soils have had the opportunity to compact fully over time. These concrete lifting tasks can often endure for two decades or more.
- Need for professional skills: Mudjacking necessitates the expertise and machinery of seasoned contractors to guarantee correct implementation and enduring outcomes.
- Advantages of Mudjacking:
- Cost-effective: Mudjacking is often more affordable than completely replacing a sunken concrete slab.
- Mudjacking causes less disruption than demolishing and replacing the whole slab by drilling small holes.
- Quick results: The process can be completed relatively quickly, allowing you to use the repaired area sooner.
- Visual: Mudjacking avoids the unsightly slab color difference associated with replacement.
- Constraints and Factors to Consider:
- Not suitable for severely damaged concrete: Mudjacking might not be effective if the concrete is heavily cracked, deteriorated, or structurally compromised. The concrete may re-settle due to the same issues, potentially leading to future settling.
- Aged concrete can be as durable as new replacements. The underlying soils have had the opportunity to compact fully over time. These concrete lifting tasks can often endure for two decades or more.
- Need for professional skills: Mudjacking necessitates the expertise and machinery of seasoned contractors to guarantee correct implementation and enduring outcomes.
Cost of Mud Jacking
The expense of mudjacking can fluctuate significantly based on numerous factors, such as the project’s size, the degree of the sunken or uneven concrete, the location, the site’s accessibility, and the materials utilized. Here are some elements that can affect the cost of a mudjacking project:
- Area Dimensions: The size of the area or the number of areas needing mud jacking can influence the cost due to the increased quantity of materials and labor required.
- Settlement Depth: The extent to which the concrete has sunk can affect the volume of slurry material needed to raise and level the slab. Greater depths may necessitate more materials and labor.
- Location Accessibility: If the depressed concrete is situated in a hard-to-reach location (like confined spaces or inaccessible areas), it might demand additional effort and specialized machinery, thereby escalating the total cost.
- Material Type: The kind of material utilized for the mud jacking slurry can impact the price. Conventional mixtures comprising soil, cement, and water may be less costly, whereas contemporary polymer-based materials might be pricier.
- Workforce Expenses: The cost of labor can fluctuate depending on the location, the contractor’s expertise, and the intricacy of the task. Competent workforce is crucial for successful mud jacking implementation.
- Extra Maintenance: There might be instances where further repairs are necessary post the mudjacking procedure, like filling up holes, mending cracks, or refurbishing the concrete. These could increase the overall expense.
- Regional Factors: The cost can significantly differ based on regional aspects, such as local labor charges, availability of materials, and market demand.
- Preliminary Work: If the site demands substantial preliminary work, like debris removal, obstacle clearance, or area cleaning, these activities can contribute to the total expense.
- Guarantee and Material Quality: Contractors providing extended guarantees or superior-quality materials may levy higher charges for their services.
- Market Dynamics: The local market’s supply and demand conditions can also influence the price. In regions where there’s a high demand for concrete repair services, the costs may be elevated.
Considering these factors, it’s difficult to give a precise cost projection without understanding the details of your project. Nonetheless, as a general guide, mud jacking expenses can vary from a few hundred dollars for a small area to several thousand dollars for larger or more intricate projects. For an exact quote in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, or nearby areas like West Bristol, Eddington, or Croydon, reach out to Concrete Chiropractor, your local mud jacking contractor. They can evaluate the situation, take into account the factors mentioned earlier, and provide you with a comprehensive cost estimate based on your requirements and location. It’s also advisable to gather multiple quotes from various contractors to compare prices and services.
- Garage Floor Raising and Coating: The Ultimate Guide - June 4, 2024
- Mudjacking Cost: 5 Factors That Affect It - April 10, 2024
- What is The Average Cost of Concrete Leveling in Belle Mead, NJ? - April 4, 2024